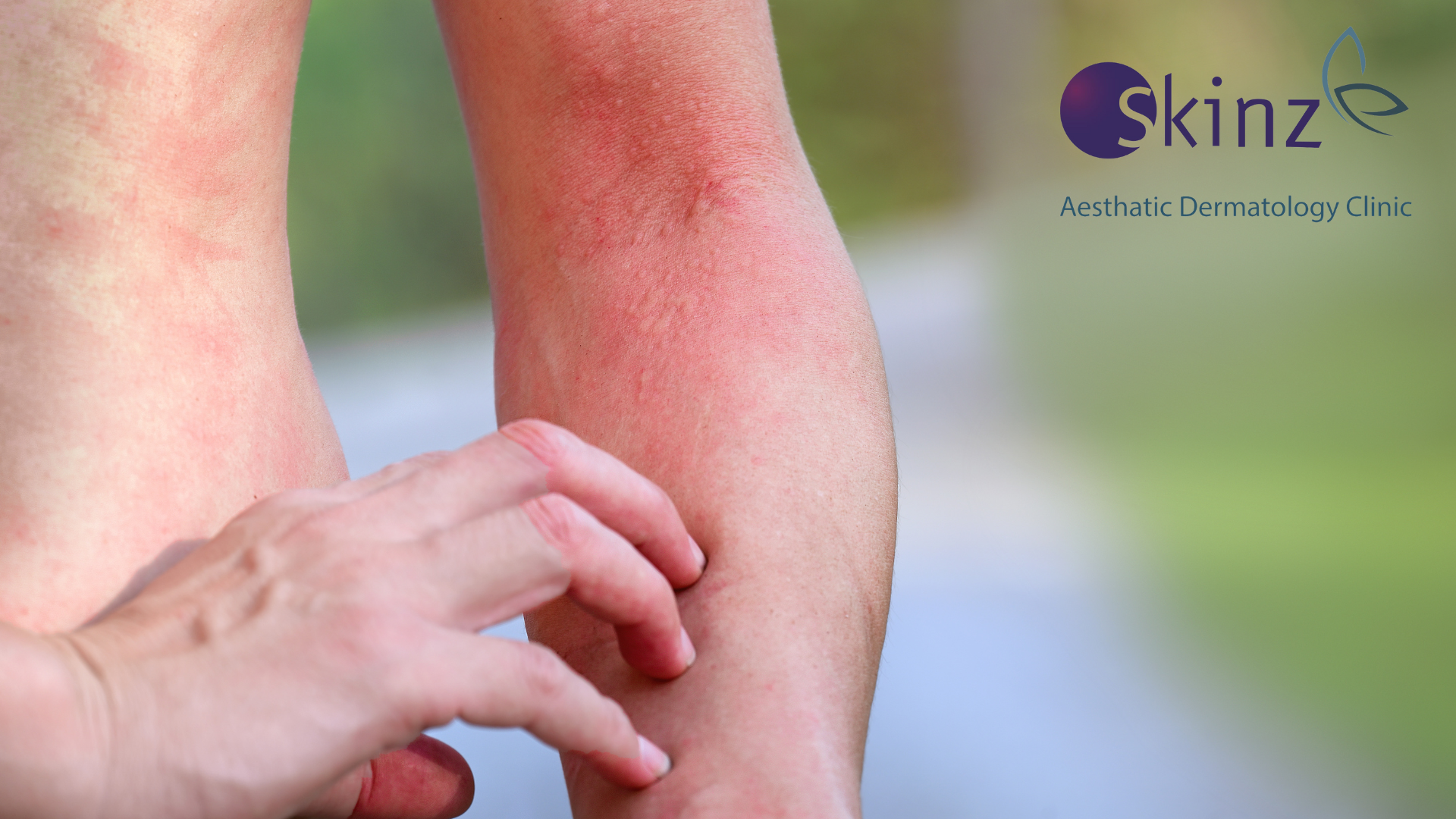
Fungal infections, while not always life-threatening, can be a real nuisance. They're more common than you might think, affecting millions of people each year. In this article, we'll explore the world of fungal infections, shedding light on their causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
What Are Fungal Infections?
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, are caused by various types of fungi. These microscopic organisms can be found in the air, soil, water, and even on our skin. Most of the time, our immune system keeps these fungi in check. However, under certain conditions, they can multiply and lead to infections.
Common Types of Fungal Infections:
Ringworm: Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by worms but by a fungus. It often appears as a red, circular rash on the skin, scalp, or nails. Ringworm is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or animal.
Yeast Infections: Candida is a type of yeast that can cause infections in various parts of the body, including the mouth (oral thrush) and the genital area (vaginal yeast infections in women and balanitis in men).
Athlete's Foot: This itchy and sometimes painful fungal infection affects the feet, particularly between the toes. It's a common ailment for athletes and those who spend a lot of time in humid environments.
Fungal Nail Infections: Fungi can invade the nails, causing them to become discolored, thickened, and brittle. This condition is often stubborn and may require prolonged treatment.
Causes of Fungal Infections:
Fungal infections can be triggered by several factors:
Weakened Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to fungal infections.
Humid Environments: Fungi thrive in warm and moist conditions, making humid climates, sweaty shoes, and damp clothing conducive to infection.
Skin Breaks: Any break in the skin, like a cut or scrape, can provide fungi with an entry point to cause an infection.
Direct Contact: Touching an infected person, animal, or contaminated surface can transmit fungal infections.
Prolonged Antibiotic Use: Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the body, allowing fungi to multiply.
Symptoms of Fungal Infections:
The symptoms of fungal infections can vary depending on the type and location of the infection. However, some common signs include:
- Itching or burning sensation
- Redness and inflammation
- Rash or blisters
- Peeling or cracking skin
- Discolored or thickened nails
- White patches in the mouth or throat
Treatment Options:
Treating fungal infections typically involves antifungal medications, which can be applied topically or taken orally. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and location of the infection.
For skin infections like ringworm and athlete's foot, over-the-counter antifungal creams are often effective. In more severe cases, prescription-strength medications may be necessary.
Oral antifungal medications are usually prescribed for nail infections and systemic fungal infections. These medications work from the inside out to combat the infection.
Preventing Fungal Infections:
Prevention is often the best strategy when it comes to fungal infections:
Maintain Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and keeping your skin clean and dry can help prevent fungal infections.
Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Refrain from sharing towels, razors, or other personal items that may carry fungi.
Wear Breathable Clothing: Choose natural, breathable fabrics to reduce moisture and prevent fungal growth.
Practice Safe Sex: Using protection during sexual activity can help prevent yeast infections.
Keep Your Environment Dry: In humid climates, use dehumidifiers, and ensure good ventilation in your living spaces.
In conclusion, fungal infections are common but manageable. With the right knowledge and precautions, you can reduce your risk and effectively treat these infections when they do occur. If you suspect you have a fungal infection, it's always advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember,